Patient 1 is a Chinese Male aged 60 years old, from the Dept. of Cardiology.
Prescription details for Patient 1:
1. GLYCERYL TRINITRATE 500MCG TABLET
– Ins: Place 1 tablet under the tongue when required
– Dur: n/a
– Qty: 1
2. ASPIRIN 100MG TABLET
– Ins: Take ONE tablet every morning
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 182
3. SIMVASTATIN 20MG TAB
– Ins: Take ONE tablet every night
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 182
4. AMLODIPINE BESILATE 5MG TAB
– Ins: Take ONE tablet every morning
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 182
5. isosorbide MONOnitrate CR 60MG TAB
– Ins: Take A HALF tablet every morning
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 91
6. biSOPROlol 2.5MG TAB (CONCOR)
– Ins: Take A HALF tablet every morning
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 91
7. FAMOTIDINE 20MG TAB
– Ins: Take ONE tablet TWO times a day
– Dur: 6 mths
– Qty: 370
General Overview:
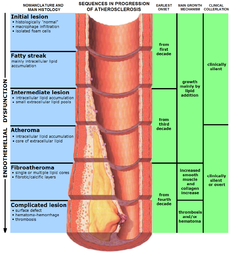
Based on the prescription above, Patient 1 seems to be on a prescription for Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD), also known as Coronary Heart Disease (CHD). IHD is the second most prevalent principal cause of death in Singapore, and is a cardiovascular disease due to atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Atherosclerosis can be defined as a progressive thickening and hardening of the walls of arteries, as a result of fat deposits on their inner lining. There are 7 risk factors associated with IHD or CHD, which can be denoted by the acronym FAITH(2)S – Family history of premature CHD (male first degree relative < 55 y/o, female < 65 y/o), Age (men > 45 y/o, women > 55 y/o), Indian ethnicity, Total cholesterol > 6.2 mmol/L or LDL > 4.1 mmol/L, HDL < 1.0 mmol/L (HDL > 1.6 mmol/L is considered as a “negative” risk factor), Hypertension (BP > 140/90 mmHg or on antihypertensive medication) and cigarette Smoking.
Angina pectoris is the most common sign of IHD. It is characterised by pain, tightness or squeezing of the chest that may radiate to the jaw, left shoulder, left back and left arm. Angina pectoris basically occurs when the myocardial oxygen demand is higher than the myocardial oxygen supply. It is also important to be able to discern angina pectoris from heartburn, as they have similar clinical presentations. Asking a patient when and how did the chest pain develop may offer clues for this cause. For example, if a patient develops chest pain after having a heavy meal or had a lot of spicy and sour food, there is a high possibility that the occurrence is due to heartburn, instead of angina pectoris. Additionally, we can also confidently rule out angina pectoris if the chest pain dissipates with antacids. If a patient is at risk for angina, it is always good to inform the patient that there are 4 main stressors that may precipitate an attack. These “4E’s” include Exertion, Emotion (fear, anger, anxiety), Extreme temperature and Eating (especially spicy food).
Pharmacologic Treatment:
Pharmacologic treatment of IHD is divided into 2 major classes, Antianginal and Vasculoprotective.
Antianginal drugs include:
– Nitrates, Beta-blockers, Calcium-channel Blockers, Ivabradine, Ranolazine
Vasculoprotective drugs include:
– Aspirin, Clopidogrel, Statins, ACE Inhibitors, ARBs
*Patient above seems to have been prescribed a triple therapy of Beta-Blocker, Nitrate and Calcium-channel Blocker, indicating that the patient is having long-term management of ischemic heart disease.
Treatment Guidelines:
A generally accepted treatment checklist for Angina is represented by the acronym “ABCDE”.
A: Aspirin and Antianginal therapy
B: Beta-blocker and Blood pressure
C: Cholesterol and Cigarette smoking
D: Diet and Diabetes
E: Education and Exercise
The 2007 Chronic Angina Focused Update of the ACC/AHA 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Chronic Stable Angina highlighted some of the following recommendations:
1. Aspirin should be started at 75-162mg a day and continued indefinitely
2. Beta-blockers as 1st choice in the absence of contraindications and continued indefinitely
3. ACEI should be started and continued indefinitely in patients with LVEF < 40%
4. CCB or long acting nitrates can be combined with Beta-blockers if initial treatment with Beta-Blocker is unsuccessful.
Patient-Specific Therapy
1. GLYCERYL TRINITRATE 500MCG TABLET
![]()
Information: GTN is a short acting nitrate useful for acute angina attacks. Nitrates belong to the class of antianginals, affecting both oxygen demand and oxygen supply of the myocardium. Myocardial oxygen demand is reduced through venodilation (by stimulating production of cGMP), hence providing sufficient blood flow to the myocardium. This is possible even in low doses. At high doses, nitrates could also increase oxygen supply due to the vasodilation of large epicardial coronary arteries and collateral vessels.
Counseling: GTN can be used to prevent angina pectoris attack or relief angina pectoris attack, hence relieving the sensation of pain and tightness in the chest due to angina. To prevent angina attacks, place 1 tablet of GTN under your tongue prior to exertion during your activity that may precipitate an attack. When used to relief angina pectoris attack, place 1 tablet of GTN under your tongue immediately when you feel the pain in your chest until the pain goes away. This will dissolve and be absorbed directly into the bloodstream. If the chest pain or tightness persists after 5 minutes despite taking 1 tablet, call the ambulance as soon as possible (in practice, we advise patients to continue taking 1 tablet after every 5 minutes if chest pain persists, until the arrival of ambulance). Delayed care of angina contributes to an increase in mortality rate. Whenever possible, try to take GTN in a sitting position instead of a standing position to minimize hypotension and dizziness. You may also experience headache and flushing when taking GTN. This is critical in elderly patients to reduce the rate of falling and chances of fracture. Although the product can last until the expiry date stated on the bottle, its shelf life is effectively reduced to 8 weeks after the bottle is opened. GTN is sensitive to both light and heat. Hence, do not remove the tablet from its amber bottle and store it in a cool dry place. Pockets on apparels are not the most desirable places to keep the medication as it is relatively warm and may affect the quality of tablets. If possible, keep it in a medication bag and take it wherever you go.
2. ASPIRIN 100MG TABLET
![]()
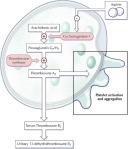 Information: Aspirin is a vasculoprotective drug. Aspirin is a COX inhibitor antiplatelet agent (other antiplatelet agents include Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel [ADP Antagonists], Dipyridamole [Phosphodiesterase inhibitor], Tirofiban, Eptifibatide, Abciximab [GP IIb/IIIa Inhibitors]). Aspirin acts as an antiplatelet agent by inhibiting platelet cyclooxygenase (COX), a key enzyme in tromboxane A2 (TXA2) generation. TXA2 is responsible for triggering platelet activation and aggregation. Aspirin is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to NSAIDs, salicylates, asthma, rhinitis, nasal polyps and should be used cautiously in patients with active gastrointestinal bleeding disorders and patients with heavy use of alcohol (ethanol). Use should also be avoided in patients with severe renal or hepatic failure.
Information: Aspirin is a vasculoprotective drug. Aspirin is a COX inhibitor antiplatelet agent (other antiplatelet agents include Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel [ADP Antagonists], Dipyridamole [Phosphodiesterase inhibitor], Tirofiban, Eptifibatide, Abciximab [GP IIb/IIIa Inhibitors]). Aspirin acts as an antiplatelet agent by inhibiting platelet cyclooxygenase (COX), a key enzyme in tromboxane A2 (TXA2) generation. TXA2 is responsible for triggering platelet activation and aggregation. Aspirin is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to NSAIDs, salicylates, asthma, rhinitis, nasal polyps and should be used cautiously in patients with active gastrointestinal bleeding disorders and patients with heavy use of alcohol (ethanol). Use should also be avoided in patients with severe renal or hepatic failure.
Counseling: Aspirin is used to prevent buildup or aggregation of platelets in the inner walls of your blood vessels. Platelets that are aggregated in blood vessels causes narrowing of the blood vessel and thrombosis (process causing formation of a fibrin blood clot), which may cause disturbance or turbulence in blood flow and may even result in total blockage. Take 1 tablet of Aspirin 100mg once in the morning after food to avoid any gastrointestinal discomfort related to aspirin. While being on this medication, look out for signs and symptoms of bleeding such as nose bleeding, coughing up of blood or having blood in your sputum, blood in urine, tea colored urine, black tarry stools, sticky and foul smelling stools accompanied with persistent abdominal pain. If these symptoms occur, visit a hospital’s emergency department immediately. As aspirin is an antiplatelet agent, you might notice that your wounds may take a longer time to stop bleeding if you experience any injury. Hence, apply pressure onto your wound if you suffered any cuts. If it is a bruise, refrain from rubbing the affected area. Most importantly, refrain from drinking alcoholic drinks while you are on aspirin, as it may cause gastrointestinal distress and bleeding.
3. SIMVASTATIN 20MG TAB (Zocor 20mg TAB)
![]()
Information: Simvastatin is a vasculoprotective drug. Statins are the only class of lipid-lowering agents that has consistently demonstrated a reduction in overall mortality. Simvastatin is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. HMG-CoA reductase catalyzes the rate limiting step n hepatic intracellular cholesterol synthesis. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase will cause increased cellular uptake of LDL molecules and lower the intravascular (blood) circulating LDL concentration effectively. The LDL goal for this patient can be set at LDL < 2.6 mmol/L. Dosing for statins can be derived from the Rule of Six. However, the Rule of Six is just an estimation, as LDL reduction is highly dependent on a patient’s lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise. Statins and cholesterol reducing medications should be taken at night as our body produces cholesterol at night.
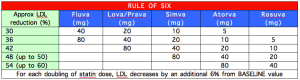
Contraindications to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor includes active liver disease (hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy), alocoholism, pregnancy and breastfeeding mothers. Among notable side effects of this class of drugs include:
a. Gastrointestinal discomfort, which will usually go away when medication is continuously taken – abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation.
b. Hepatotoxicity – This is because statin is cleared through the liver. If AST or ALT increase to > 3 times the UNL and persist, dose reduction or drug withdrawal is recommended. Hence, monitoring of LFT 6-12 weeks after initiation or increase in dose, then at least once annually is required. If LFT > 3x UNL, it is recommended to stop statin therapy and only be reintroduced at a lower dose when LFT is normalized.
c. Myopathy and Rhabdomyolysis (Increase in Creatinine Kinase > 10 times UNL with Creatinine elevation) – Usually presented with brown urine and described by general unexplained muscle pain. Higher risk in patients on high statins dose, old age, renal impairment, and LDL-lowering agent combination therapy such as nicotinic acid and fibrates.
Counseling: Simvastatin is a medication used to reduce the levels of bad cholesterol in your body. This is important in the management of your heart condition, as it helps to prevent the accumulation of cholesterol in the inner walls of your blood vessels, which may lead to blood clots. Take 1 tablet of Simvastatin 20mg every night as our body produces cholesterol at night. Do not take this medication with alcohol as it will severely damage your liver. You may experience some common side effects such as stomach discomfort and flatulence while taking Simvastatin. These side effects should go away as you continue with this medication. However, do take note of symptoms such as brown coloured urine, yellowing of eyes or skin, and generalized, unexplained muscle ache accompanied by fever. If these symptoms arise, stop your medication and visit a hospital’s emergency department immediately. Lastly, please include a reminder on you and your caregiver’s phone or calendar for the date of your next doctor’s appointment. This is important for us to be able to monitor the effect of Simvastatin on your cholesterol control and liver function.
4. AMLODIPINE BESILATE 5MG TAB (Norvasc 5mg TAB)
![]()
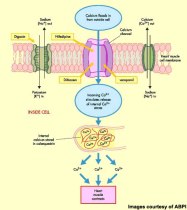 Information: Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB) is an antianginal agent. It can be divided into Dihydropyridines (Amlodipine, Nifedipine) and Non-Dihydropyridines (Verapamil, Diltiazem). CCB block the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into cardiac muscles and vascular smooth muscles by binding to L-type calcium channels. CCB is an antianginal medication that affects both oxygen supply and oxygen demand of cardiac muscles. Oxygen supply is increased due to the dilation of coronary arteries causing reduced coronary vascular resistant AND increased coronary blood flow. On the other hand, myocardial oxygen demand is reduced due to a reduction in SYSTEMIC vascular resistance and arterial blood pressure (vasodilation of systemic arteries) and a negative inotropic effect causing decreased cardiac contractility. However, Non-Dihydropyridines have a more pronounced effect in slowing AV conduction and SA node automaticity, hence decreasing heart rate, as compared to Dihydropyridines. This is important to avoid prescribing Non-Dihydropyridines to patients who are concurrently on Beta-Blockers, as this will severely reduce the patient’s heart rate. Nifedipine is a short-acting dihydropyridine that should be avoided due to its powerful peripheral vasodilating effect, which may cause reflex tachycardia.
Information: Calcium Channel Blocker (CCB) is an antianginal agent. It can be divided into Dihydropyridines (Amlodipine, Nifedipine) and Non-Dihydropyridines (Verapamil, Diltiazem). CCB block the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into cardiac muscles and vascular smooth muscles by binding to L-type calcium channels. CCB is an antianginal medication that affects both oxygen supply and oxygen demand of cardiac muscles. Oxygen supply is increased due to the dilation of coronary arteries causing reduced coronary vascular resistant AND increased coronary blood flow. On the other hand, myocardial oxygen demand is reduced due to a reduction in SYSTEMIC vascular resistance and arterial blood pressure (vasodilation of systemic arteries) and a negative inotropic effect causing decreased cardiac contractility. However, Non-Dihydropyridines have a more pronounced effect in slowing AV conduction and SA node automaticity, hence decreasing heart rate, as compared to Dihydropyridines. This is important to avoid prescribing Non-Dihydropyridines to patients who are concurrently on Beta-Blockers, as this will severely reduce the patient’s heart rate. Nifedipine is a short-acting dihydropyridine that should be avoided due to its powerful peripheral vasodilating effect, which may cause reflex tachycardia.
Counseling: Amlodipine is a medication used to protect your heart by increasing oxygen supply to your heart muscles, while also helping to lower your blood pressure. Take 1 tablet of 5mg Amlodipine every morning with or without food. Please avoid from activities requiring coordination such as driving or cooking until you are fully aware and gotten use to the effects of Amlodipine on your body, as it may cause dizziness. Similarly, take your time if you intend to stand up from a lying or sitting down position to avoid sudden drowsiness while getting up. Amlodipine may also cause some common side effects such as fatigue, headaches, abdominal pain, swelling, flushing or nausea. Flushing happens as the medication lowers your blood pressure by opening up your blood vessels. Swelling usually happens in your feet and can be improved by putting a pillow beneath your feet when you sleep. If such symptoms persist or worsens when you continue taking the medication, please alert your doctor.
5. isosorbide MONOnitrate CR 60MG TAB (Imdur 60mg TAB)
Information: Isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) is an antianginal drug belonging to the class of long-acting (usually used as a prophylactic) nitrates. ISMN is the major active metabolite of ISDN. Nitrates can be considered prodrugs as they require Sulfhydryl groups (SH) to facilitate the biotransformation of organic nitrates to Nitric Oxide (NO). NO then stimulates Guanylyl cyclase to convert to cGMP. Increased intracellular cGMP inhibits calcium entry into the cell, thereby decreasing intracellular calcium concentrations and causing smooth muscle relaxation. Nitrates primarily reduces myocardial oxygen demand via venodilation, hence reducing venous pressure and decreases ventricular preload. Subsequently, this reduces ventricular wall stress and oxygen demand by the heart. At high doses, nitrates increases oxygen supply by dilating large epicardial coronary arteries. Headache due to nitrate tolerance is often a common side effects among patients. Although the mechanism of action of nitrate tolerance is not fully known, it may be caused by the depletion od SH over time. Hence, nitrate-free periods are required to replenish these SH groups by either maintaining nitrate-free intervals of 10-12 hours a day or using lower doses of nitrate. ISMN can be dosed once daily, hence providing both convenience and a nitrate free-period of 12 hours (duration of action of Imdur CR is 12 hours). Vasodilation might also cause dizziness in patients. Concurrent use of nitrates with PDE-5-Inhibitors such as Sildenafil (Viagra) within 24 hours (48 hours if Tadalafil [Cialis] is used) is contraindicated, as it will cause severe hypotension that may be fatal.
 Counseling: ISMN is a medication used to protect your heart by reducing its workload and prevent chest pain. This will ensure that your heart muscles are not overworked and is provided sufficient blood flow and oxygen. Take half a tablet of ISMN 60mg every morning with or without food. You can break the tablet into half following the scoreline on the tablet (usually CR tablets cannot be broken. Imdur CR is one of the exceptions, as it has a scoreline on the tablet. ISMN is usually started at 60mg daily, but can be titrated down to 30mg daily especially if patient is not tolerant to the side effects of throbbing headaches), but do not crush or chew the tablet as there is a protective cover over this tablet to slowly release the medicine into the body. This medication might cause some lightheadedness. Hence, take your time if you intend to stand up from a sitting or lying down position to avoid from sudden dizziness that may lead to fall. You might have experience headache side effects when taking this medication in the past. Although the dose has been reduced, you might still experience some headache. Please alert your doctor if your headache persists or worsens as you continue to take this medication. Very importantly, do not take Sildenafil or Viagra while being on this medication.
Counseling: ISMN is a medication used to protect your heart by reducing its workload and prevent chest pain. This will ensure that your heart muscles are not overworked and is provided sufficient blood flow and oxygen. Take half a tablet of ISMN 60mg every morning with or without food. You can break the tablet into half following the scoreline on the tablet (usually CR tablets cannot be broken. Imdur CR is one of the exceptions, as it has a scoreline on the tablet. ISMN is usually started at 60mg daily, but can be titrated down to 30mg daily especially if patient is not tolerant to the side effects of throbbing headaches), but do not crush or chew the tablet as there is a protective cover over this tablet to slowly release the medicine into the body. This medication might cause some lightheadedness. Hence, take your time if you intend to stand up from a sitting or lying down position to avoid from sudden dizziness that may lead to fall. You might have experience headache side effects when taking this medication in the past. Although the dose has been reduced, you might still experience some headache. Please alert your doctor if your headache persists or worsens as you continue to take this medication. Very importantly, do not take Sildenafil or Viagra while being on this medication.
6. biSOPROlol 2.5MG TAB (CONCOR)
![]()
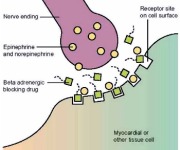 Information: Bisoprolol is an antianginal agent belonging to the class of Beta-Blockers (BB). Beta-blockers bind to beta-adrenoceptors thereby blocking the binding of norepinephrine and epinephrine to these receptors. As a result, BB inhibits normal sympathetic effects of these receptors. Beta-1 receptors are found primarily in the myocardium, while Beta-2 receptors are mainly distributed in the vascular and bronchial smooth muscles. Blocking of Beta-1 receptors causes a reduction in chronotropy (heart rate) and inotropy (contractility). Blocking of Beta-2 receptors causes bronchoconstriction, which may trigger asthma in patients with unstable asthma conditions. In general, 2nd generation BB such as bisoprolol is more selective in blocking Beta-1 receptors. However, this selectivity reduces with higher doses. Some BB such as Acebutolol has Intrinsic Sympathomimetic Activity (ISA), which means they mimic effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine causing an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. Hence, BB with ISA should be avoided in anginal therapy. A general rule for BB therapy is to START LOW & GO SLOW. The goal of BB therapy is to titrate dose to a resting heart rate of 50-60 beats/min and a maximum exercise heart rate of less than 100 beats/min. This should be monitored every 2 weeks during initiation of BB therapy for angina. When considering to stop BB therapy, ensure that it is tapered over at least 2 days to prevent withdrawal problems such as palpitations, rise in blood pressure and recurrence of angina pains. Lastly, fatigue is a very common side effect especially at the start of BB therapy. It is important to manage your patient’s expectations and reassure them that the fatigue will go away as the body gets used to the medication.
Information: Bisoprolol is an antianginal agent belonging to the class of Beta-Blockers (BB). Beta-blockers bind to beta-adrenoceptors thereby blocking the binding of norepinephrine and epinephrine to these receptors. As a result, BB inhibits normal sympathetic effects of these receptors. Beta-1 receptors are found primarily in the myocardium, while Beta-2 receptors are mainly distributed in the vascular and bronchial smooth muscles. Blocking of Beta-1 receptors causes a reduction in chronotropy (heart rate) and inotropy (contractility). Blocking of Beta-2 receptors causes bronchoconstriction, which may trigger asthma in patients with unstable asthma conditions. In general, 2nd generation BB such as bisoprolol is more selective in blocking Beta-1 receptors. However, this selectivity reduces with higher doses. Some BB such as Acebutolol has Intrinsic Sympathomimetic Activity (ISA), which means they mimic effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine causing an increase in blood pressure and heart rate. Hence, BB with ISA should be avoided in anginal therapy. A general rule for BB therapy is to START LOW & GO SLOW. The goal of BB therapy is to titrate dose to a resting heart rate of 50-60 beats/min and a maximum exercise heart rate of less than 100 beats/min. This should be monitored every 2 weeks during initiation of BB therapy for angina. When considering to stop BB therapy, ensure that it is tapered over at least 2 days to prevent withdrawal problems such as palpitations, rise in blood pressure and recurrence of angina pains. Lastly, fatigue is a very common side effect especially at the start of BB therapy. It is important to manage your patient’s expectations and reassure them that the fatigue will go away as the body gets used to the medication.
Counseling: Bisoprolol is a medication used to protect your heart by slowing down your heart rate thereby reducing its workload. Take half a tablet of bisoprolol 2.5mg tablet every morning with or without food. This medication may cause some slight fatigue as it helps to reduce your heart rate. However, please continue taking the medication as it will allow your body to adapt to it and providing more benefits to your cardiac health in the long run. Bisoprolol might also reduce your blood pressure causing dizziness and drowsiness. Try to avoid standing up quickly from a sitting or standing position to avoid unwanted falls.
7. FAMOTIDINE 20MG TAB (Famotin 20mg TAB)
![]()
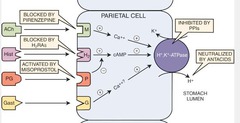 Information: Famotidine is a Histamine H2 Antagonist. It competitively inhibits histamine at H2 receptors of the gastric parietal cells, thereby inhibiting gastric acid secretion. It is used to prevent gastric and duodenal ulcers, and erosive esophagitis in patients taking low dose aspirin for vascular protection, according to results from the phase 3 FAMOUS trial published in The Lancet in July 2009.
Information: Famotidine is a Histamine H2 Antagonist. It competitively inhibits histamine at H2 receptors of the gastric parietal cells, thereby inhibiting gastric acid secretion. It is used to prevent gastric and duodenal ulcers, and erosive esophagitis in patients taking low dose aspirin for vascular protection, according to results from the phase 3 FAMOUS trial published in The Lancet in July 2009.
Counseling: Famotidine is a medication used to prevent gastric bleeding and ulcers while taking daily doses of aspirin. Take 1 tablet of Famotidine 20mg in the afternoon and another tablet at night before bedtime. You may experience some common side effects such as headache, diarrhea and constipation. These are usually mild and should go away with continuous use. However, if these symptoms persist or worsens, alert your doctor. You can take this medication concurrently with antacids if you experience heartburn. However, if the heartburn does not subside and you feel that the pain is radiating towards the jaw, shoulders, back or left arm, indicating the possibility of an angina attack, place a GTN tablet under your tongue.
Non-Pharmacological Therapy (DEWS)
1. Diet modification – Increase consumption of fruit, vegetables, grains and cereals. In terms of meat, try to prefer skinless poultry, fish and lean meats while abstaining from fats. Dairy products should also be low-fat. Simple carbohydrates especially from rice rice should be reduced, while alcohol should be completely avoided.
2. Exercise – At least 4 hours a week of moderate exercise can reduce risk of cardiovascular disease. In the elderly, they can also perform less vigorous activities such as walking or taichi.
3. Weight reduction – Aim to reduce weight to maintain a healthy BMI of 19 to 24.9 kg/m2
4. Smoking cessation – If the patient smokes, advise patient to gradually quit smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes smoked daily. Smoking increases the risk of IHD and may precipitate angina attacks.
Important Notes:
1. Definition of Atherosclerosis
2. FAITH(2)S
3. 4E’s
4. Antianginal drugs
5. Vasculoprotective drugs
6. ABCDE angina therapy guideline
7. Rule of Six
8. LDL Goal for patients with high risk for CHD
9. Rhabdomyolysis in statins
10. Dihydropyridines and Non-dihydropyridines and which one is preferred if concurrent BB therapy
11. Goal of BB therapy
12. FAMOUS trial recommendation
13. DEWS non-pharmacological therapy
14. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()